Superiority
APPLICATIONS
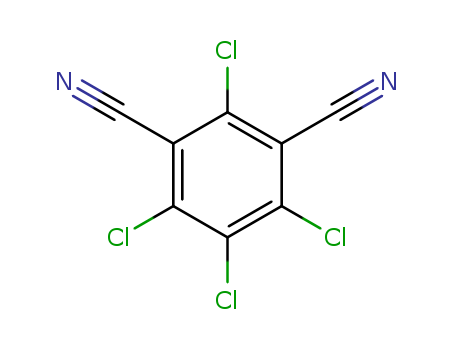
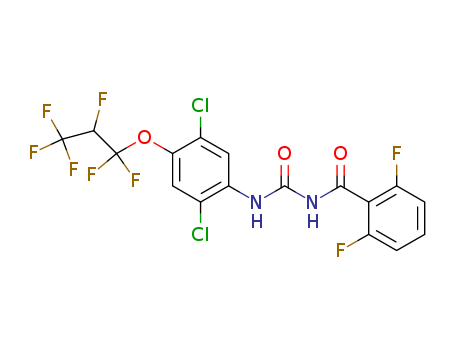
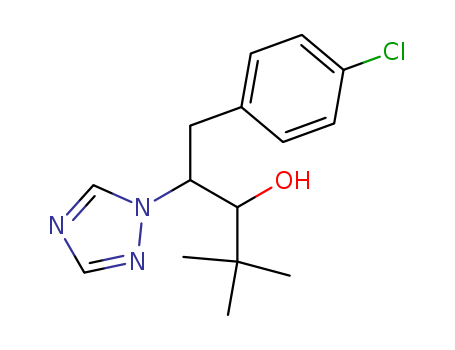
Biochemistry Mode of action probably involves an interaction with octopamine receptors in the tick nervous system, causing an increase …
Details
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Mode of action probably involves an interaction with octopamine receptors in the tick nervous system, causing an increase in nervous activity. Mode of action Non-systemic, with contact and respiratory action. Expellent action causes ticks to withdraw mouthparts rapidly and fall off the host animal. Uses Control of all stages of tetranychid and eriophyid mites, pear suckers, scale insects, mealybugs, whitefly, aphids, and eggs and first instar larvae of Lepidoptera on pome fruit, citrus fruit, cotton, stone fruit, bush fruit, strawberries, hops, cucurbits, aubergines, capsicums, tomatoes, ornamentals, and some other crops. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide to control ticks, mites and lice on cattle, dogs, goats, pigs and sheep. Phytotoxicity At high temperatures, young capsicums and pears may be injured. Formulation types EC; PO; WP.